Terms
Not sure what we mean?
Don’t worry, we are here to help. Read through our list of terms and definitions below.
Gender:
Sex
Refers to a set of biological attributes in humans and animals. It is primarily associated with physical and physiological features including chromosomes, gene expression, hormone levels and function, and reproductive/sexual anatomy. Sex is usually categorized as female or male but there is variation in the biological attributes that comprise sex and how those attributes are expressed.
Gender
Refers to the socially constructed roles, behaviours, expressions and identities of girls, women, boys, men, and gender diverse people. It influences how people perceive themselves and each other, how they act and interact, and the distribution of power and resources in society. Gender is usually conceptualized as a binary (girl/woman and boy/man) yet there is considerable diversity in how individuals and groups understand, experience, and express it.
Gender Identity
A person’s internal and deeply felt sense of being a man or woman, both or neither. A person’s gender identity may or may not align with the gender typically associated with their sex.
Gender Expression
The way in which people publicly present their gender through aspects such as dress, hair, make-up, body language, and voice.
Women
All people who identify as women, whether they are cisgender or transgender women.
Men
All people who identify as men, whether they are cisgender or transgender men.
Gender-Diverse
Refer to individuals who do not identify as exclusively male or exclusively female (for example, individuals who are non-binary or two-spirit).
Non-Binary
Person whose gender identity does not align with a binary understanding of gender such as man or woman. A non-binary person may identify as neither a man nor a woman, both, or anywhere along the gender spectrum.
Transgender
A person whose current gender does not align with the sex that they were assigned at birth.
Two-Spirit Persons
Umbrella term for some Indigenous people who identify as having both a female and male spirit within them or whose gender identity, gender expression, sexual orientation or spiritual identity is not limited by the binary classification of gender as woman or man.
Cisgender
People whose gender identity matches the sex that they were assigned at birth.
Feminism:
Feminism
Refers to political, social, and intellectual movements working towards the goal of equality for individuals of all genders. There have always been individuals who have fought against the limits that their society placed on people based on their gender. However, feminism as a political, social and intellectual movement only started in the mid-19th century in Europe. French philosopher Charles Fourier is credited with first using the term “féminisme” in the 1830s, and “feminist” first appeared in the Oxford English Dictionary in 1852. Since this time, feminism as a movement has spread across the world, including to Canada, in many different forms.
Intersectionality
The interconnected nature of various social or identity factors, such as sex, gender, age, race, ethnicity, Indigenous identity, economic status, immigrant status, sexual orientation, disability, and geography, as they apply to a given individual or group, viewed as impacting experiences of discrimination or disadvantage. For example, intersectionality recognizes that Indigenous women hold more than one identity. They are women and share some common experiences with other women, and they are Indigenous and have shared experiences with Indigenous men. Trying to understand Indigenous women’s experiences by focusing only on sex or only on Indigenous identity prevents us from seeing how these identities intersect to create a unique lived experience for Indigenous women that is different from the experiences of Indigenous men and non-Indigenous women.
Patriarchy
A system of society or government where men predominate in roles of political leadership, moral authority, social privilege and control of property.
Patriarchal
Characteristic of a system of society or government where men predominate in roles of political leadership, moral authority, social privilege and control of property.
Urbanism:
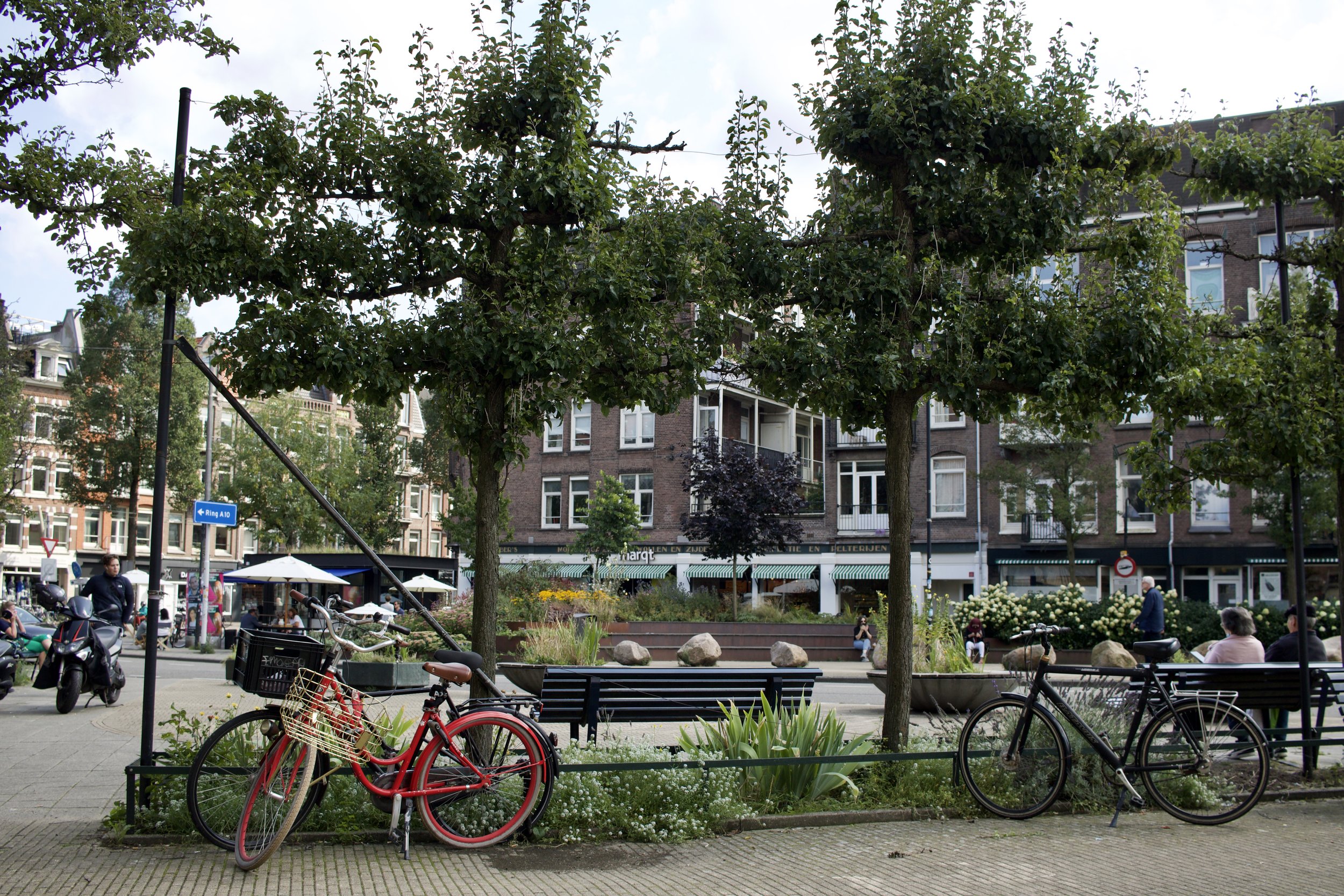
Urbanism
Is the study of how inhabitants of urban areas, such as towns and cities, interact with the built environment.
New Urbanism
A planning and development approach based on the principles of how cities and towns had been built for the last several centuries: walkable blocks and streets, housing and shopping in close proximity, and accessible public spaces. In other words: New Urbanism focuses on human-scaled urban design.
Urbanist
Someone that wants more people (of all types) to have equal access to housing variety (apartments, townhomes, backyard cottages, houses, duplexes, etc.), more ways to get around (transit, walking, bicycling, ride-share, vanpool, etc.), more to see and do (parks, cafes, bars, museums, shops, etc.), and to have more grassroots influence on city government.
Built Environment
The term is used when referring to those surroundings created for humans, by humans, and to be used for human activity. Examples would include cities, buildings, urban spaces, walkways, roads, parks, etc.
Gentrification
Changed in character by wealthier people moving in, improving housing, and attracting new businesses, typically displacing current inhabitants in the process.